Submit feedback
What is a Quick Joint?
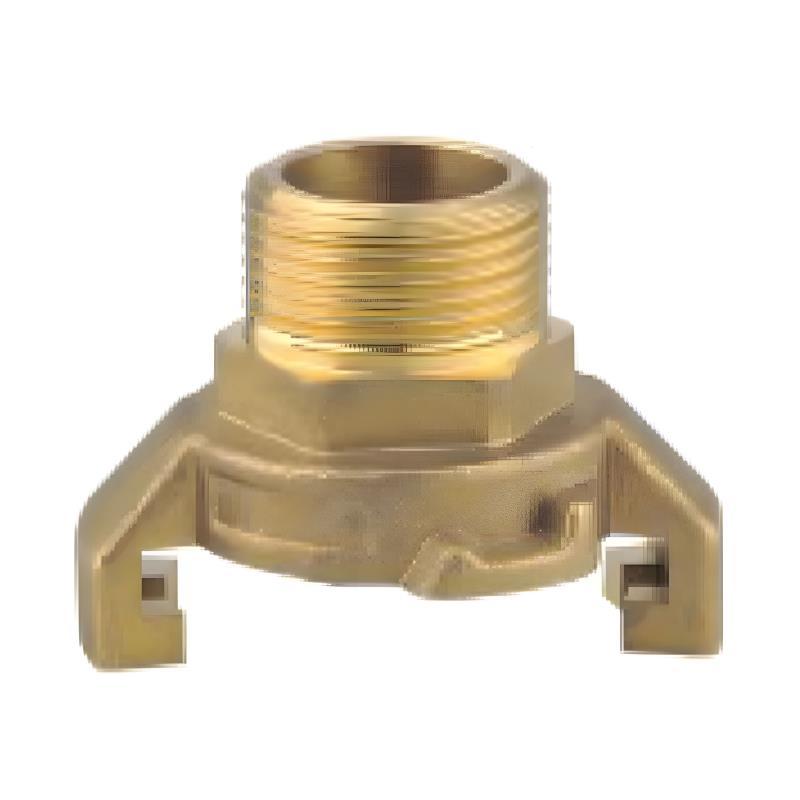
Custom quick connect ball joint Manufacturer
A quick joint is a mechanical device designed to connect or disconnect two systems or components rapidly without the need for additional tools or excessive effort. The primary function of a quick joint is to create a secure connection between two parts, typically involving fluid or gas lines, electrical systems, or pneumatic systems. Quick joints are designed for ease of use, allowing operators to make connections quickly while minimizing the risk of leaks, contamination, or other operational issues.
The basic working principle behind a quick joint is its ability to establish a tight, reliable seal with minimal user intervention. The connection is often achieved through a snap-on, click, or push-to-lock mechanism that automatically ensures the joint is firmly in place. This ease of use is one of the reasons why quick joints are widely adopted across various industries, from automotive to manufacturing, and even in home appliances.
How Quick Joints Work?
Quick joints typically consist of two main parts: the male and female components. The male end has a nozzle or coupling that fits into the female counterpart, which contains a locking mechanism to secure the connection. Once the male part is inserted into the female part, the locking mechanism automatically engages, ensuring a strong, leak-proof seal. This mechanism might include a spring-loaded system, a ball-locking system, or a latch, depending on the design of the quick joint.

The disconnection process is equally straightforward. To separate the two components, users simply need to release the locking mechanism, often by pressing a button, pulling a lever, or twisting the connection. This simplicity of operation significantly reduces downtime, making quick joints particularly valuable in environments where efficiency and speed are critical.
Types of Quick Joints
Quick joints come in various types, each designed for specific applications and industries. Below are the most common forms of quick joints:
Pneumatic Quick Joints
Pneumatic quick joints are primarily used in systems that carry compressed air. These joints are found in tools, machinery, and vehicles, enabling operators to quickly connect or disconnect air lines. They are designed to handle pressures and temperatures that can vary significantly, making them ideal for industries such as construction, automotive repair, and manufacturing.
Hydraulic Quick Joints
In industries that rely on hydraulic systems, hydraulic quick joints play a crucial role. These joints are designed to facilitate fast connections for high-pressure fluid systems. They are commonly used in heavy machinery, construction equipment, and agricultural machinery, where rapid fluid changes are required. Hydraulic quick joints are built to withstand significant pressure, ensuring that fluids are transferred without leakage or damage to the system.
Electrical Quick Joints
Electrical quick joints are specifically designed for quick, reliable electrical connections. These joints are often used in power distribution systems, electrical machinery, and appliances. With a quick electrical joint, technicians can efficiently connect or disconnect wires or circuits, reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency. Electrical quick joints can be used in a wide range of voltages and are engineered to ensure minimal contact resistance and stable electrical flow.
Automotive Quick Joints
In the automotive industry, quick joints are used in various applications, including fuel lines, air conditioning systems, and engine components. These joints allow for quick repairs or replacements of automotive parts, minimizing the need for extensive downtime in service shops or on the production line. They are designed to ensure compatibility with the materials used in automotive manufacturing, such as rubber, plastic, and metal while providing a secure and reliable connection.
Applications of Quick Joints
The versatility of quick joints means they are used across numerous sectors and applications. In industrial settings, quick joints facilitate smooth production processes by enabling rapid connection and disconnection of pneumatic and hydraulic lines. In automotive service, they reduce the time needed to perform maintenance tasks, such as replacing brake fluid or refilling cooling systems. Similarly, in agriculture, quick joints are used to connect irrigation systems and facilitate the easy transfer of fluids.
Another key application of quick joints is in the medical industry, where quick connectors are used in hospital equipment, including oxygen masks, IV fluids, and dialysis machines. These systems require secure, leak-proof connections to ensure patient safety and quick joints offer a reliable solution that allows healthcare workers to work efficiently.
In-home settings, quick joints are often found in garden hoses, allowing users to easily connect and disconnect water lines. This simple convenience extends beyond industrial and commercialuse, demonstrating the widespread utility of these devices.
Advantages of Quick Joints
The main advantage of using quick joints is their time-saving capability. Workers can save a significant amount of time by eliminating the need for tools and complex procedures when making connections. This results in more efficient work environments and can contribute to overall productivity improvements in various industries.
Furthermore, quick joints ensure a higher level of safety and reliability. Because they are designed to lock into place, they prevent accidental disconnections and minimize the risk of leaks or contamination. These features are especially important in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and oil and gas, where integrity and safety are of the utmost importance.
In conclusion, quick joints are essential components that contribute significantly to industrial, automotive, and even domestic operations. Their ease of use, speed, and reliability make them an indispensable tool across a wide range of applications. Whether connecting pneumatic, hydraulic, or electrical systems, quick joints streamline processes, reduce downtime, and improve overall efficiency. As technology advances and industries continue to evolve, the role of quick joints will only become more critical, solidifying their place as a key solution in the modern world of connections.
 +86-13989680588
+86-13989680588 graylin@hongjiavalve.com
graylin@hongjiavalve.com